

The sensory division, also called the afferent division, contains neurons that receive signals from the tendons, joints, skin, skeletal muscles, eyes, nose, ears and tongue, and many other tissues and organs. The somatic nervous system (SNS) consists of sensory and motor nerve divisions. The ANS is further divided by function into sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. The PNS is subdivided into the somatic nervous system (SNS) and the autonomic nervous system (ANS).

The nervous system of the human body is divided into the central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the spinal cord and brain, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), consisting of all the nerves that connect the CNS with organs, muscles, blood vessels and glands. There are two types of neurons found in the SNS: sensory neurons, which typically have long dendrites and short axons, and carry messages from sensory receptors to the CNS, and motor neurons, which have a long axon and short dendrites and transmit signals from the CNS to muscles or glands. Neurons are also the longest cells of the body, a single axon can be several feet long. The average adult brain contains about 100 billion neurons. Both axons and dendrites are surrounded by a white protective coating called the myelin sheath. The dendrites receive information from other nearby cells and transmit the signals to the soma and the axon carries signals away from the neuron. NeuronsĪ neuron consists of a cell body, the soma, which contains the nucleus and surrounding cytoplasm, several short thread-like projections, called dendrites, and of one long filament, called the axon. Neurons transmit nerve signals and are surrounded by glial cells, that provide mechanical and physical support as well as electrical insulation between neurons.
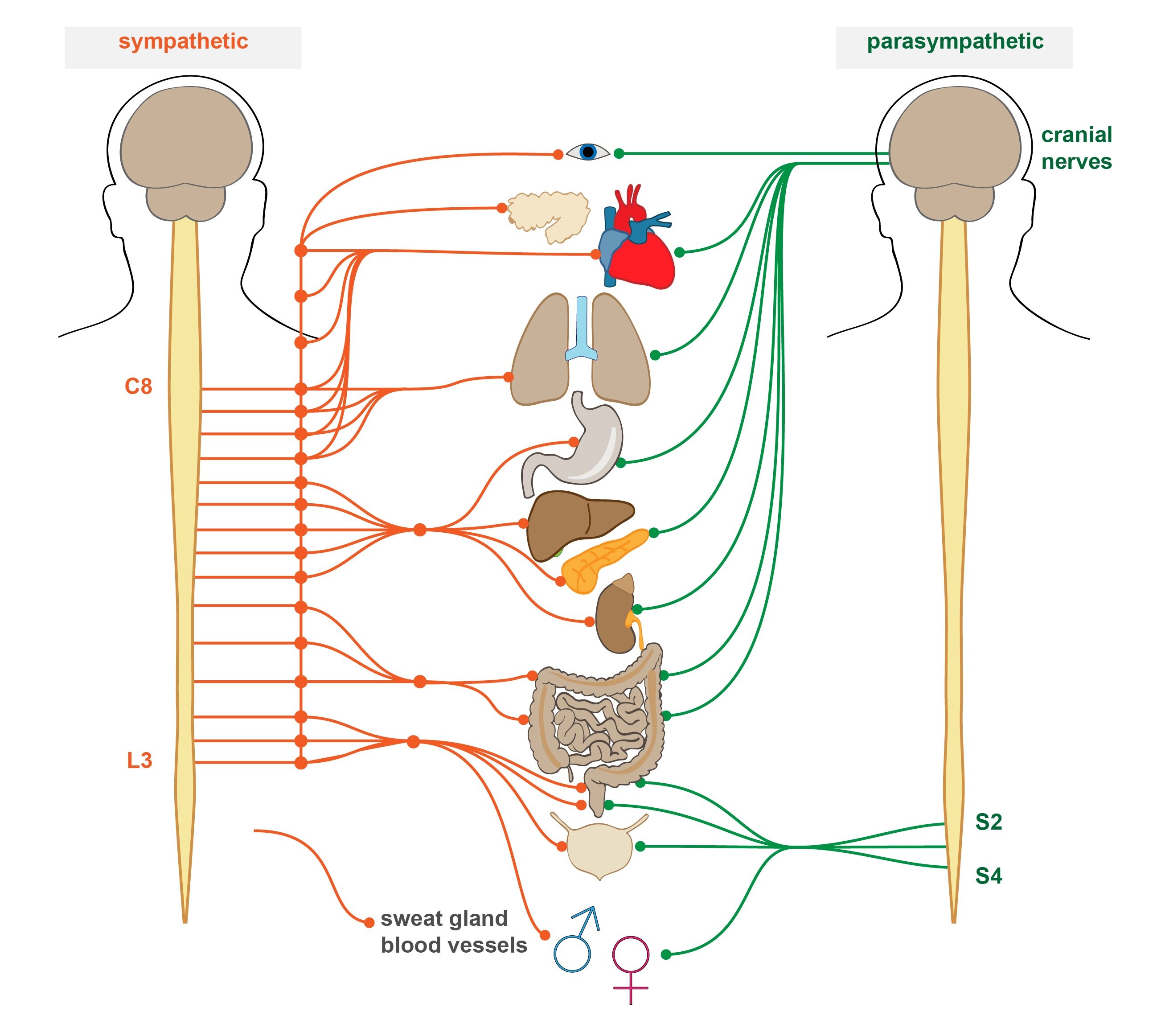

Description Nervous tissueĪll nervous tissue-including that of the SNS-consists of two main cell types: neurons and glial cells. Sensory nerves convey nerve impulses from the sense organs to the central nervous system (CNS), while motor nerves convey nerve impulses from the CNS to skeletal muscle effectors. It includes both sensory and motor nerves. The SNS controls voluntary activities, such as movement of skeletal muscles. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system.The somatic nervous system (SNS) is a division of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The ANS is classically divided into two subsystems: the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) and sympathetic nervous system (SNS). Whereas most of its actions are involuntary, some, such as breathing, work in tandem with the conscious mind. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiratory rate, salivation, perspiration, pupillary dilation, micturition (urination), and sexual arousal. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system, functioning largely below the level of consciousness and controlling visceral functions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
